Swimming Nutrition

swimming nutrition
Swimming is one of the most difficult sports in terms of meeting your bodies nutritional needs. Whether it be a short distance or long distance swimmer, swimmers burn through an extraordinary amount of calories and micronutrients. Swimmer rely on power, speed and endurance, not only in competition but practice.
Most of the energy demands of swimming surround the demands of practice and peaking. Michael Phelps was famously quoted as eating over 10,000 calories a day just to maintain his energy levels and muscle mass. Understanding the demands of swimming on the body is just the first step in ensuring optimum performance.
Nutrition For Swimming
Swimming is one of the most difficult sports in terms of meeting your bodies nutritional needs. Whether it be a short distance or long distance swimmer, swimmers burn through an extraordinary amount of calories and micronutrients. Swimmers rely on power, speed and endurance, not only in competition but practice.
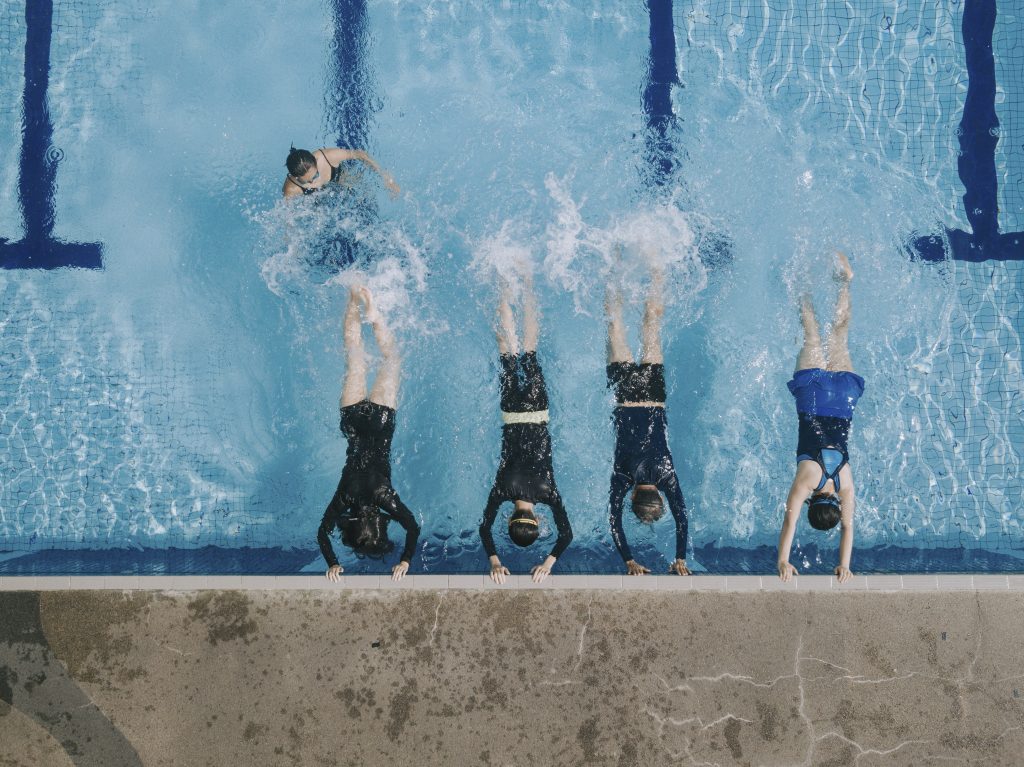
Lactic acid build-up and cramping is also a big concern for many swimmers. With proper nutrition and supplementation cramps and muscle fatigue due to lactic acid can be greatly reduced or eliminated all together. Our certified staff has under gone some of the most rigorous training available, including the USADA drug testing program. This gives our clients the peace of mind that our programs and supplement recommendations will never interfere with high school, NCAA or professional regulations.
In addition, proper hydration is crucial for athletic performance. Dehydration can cause over-heating, reduced reaction time, cramps, muscle tears, decreased strength and endurance. Hydration isn’t just for practice and games, staying hydrated all day is very important.
CONTACT US
Why Should You Join Champion Athletes Swimming Nutrition Program
- Sports Specific- We take into consideration the energy and hydration demands of each individual sport. With all of our swimmers we also take their specific races and whether they are in their short or long season into consideration.
- 100% customized- Each of our plans is 100% customized for each one of our clients.
- Foods you like and eat- Unlike other nutritionists that hand you a food journal and generic foods, we design our programs with foods that you enjoy and that are readily available to you and your family.
- Support 7 days a week- We provide daily coaching. Each of our clients has access via text, phone and email to our staff every day. If you have a problem, cheat on the plan or have a question you can reach out at any time! We will help you every step of the way.

 Swimming is one of the most difficult sports in terms of meeting your bodies nutritional needs. Whether it be a short distance or long distance swimmer, swimmers burn through an extraordinary amount of calories and micronutrients. Swimmer rely on power, speed and endurance, not only in competition but practice.
Swimming is one of the most difficult sports in terms of meeting your bodies nutritional needs. Whether it be a short distance or long distance swimmer, swimmers burn through an extraordinary amount of calories and micronutrients. Swimmer rely on power, speed and endurance, not only in competition but practice. The average high level swimmer needs to consume around 4,500 calories a day in order to maintain optimal performance. The primary fuel for swimming is carbohydrates. Swimmers should eat primarily complex carbohydrates for meals and simple carbohydrates for a snack shortly before practice and competitions. In order to compete optimally a swimmer requires 65% to 73% percent of their daily caloric intake to come from carbohydrates, 12-15% from protein and 15-20%% percent from fat.
The average high level swimmer needs to consume around 4,500 calories a day in order to maintain optimal performance. The primary fuel for swimming is carbohydrates. Swimmers should eat primarily complex carbohydrates for meals and simple carbohydrates for a snack shortly before practice and competitions. In order to compete optimally a swimmer requires 65% to 73% percent of their daily caloric intake to come from carbohydrates, 12-15% from protein and 15-20%% percent from fat.